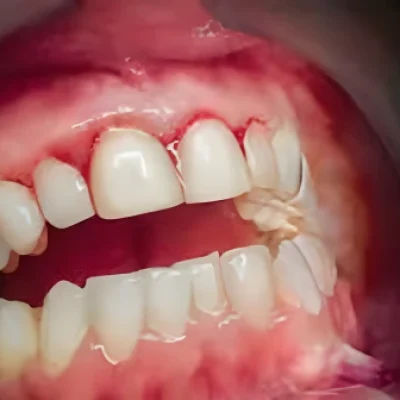
Gum disease is an infection of the tissues surrounding and supporting the teeth. It is a common oral health problem and can range from mild (gingivitis) to severe (periodontitis).
The main cause of gum disease is plaque buildup on teeth. Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that constantly forms on teeth. If not removed by brushing, flossing, and regular dental cleanings, plaque can harden into tartar and cause inflammation of the gums.
The early stages of gum disease may not have any symptoms, but as it progresses, the following signs may become noticeable:
1. Non-Surgical Treatment
2. Surgical Treatment
The best way to prevent gum disease is to maintain good oral hygiene, including brushing and flossing regularly and visiting the dentist for regular cleanings and check-ups. Additionally, quitting smoking and managing stress can also help prevent gum disease.

© 2023-25 Website Developed & Maintained by iBS